Filter By
Open Opportunities
STANDARD CALL FOR PROPOSALS
Under NAVISP Element 2, the permanent Standard Call for Proposals focuses on developing innovative competitive products in the Position, Navigation and Timing domain, in particular, Satellite Navigation.
The objective is to boost Participant States industrial competitiveness in the fast- evolving Position, Navigation, and Timing sector.
NAVISP Element 2 welcomes proposals from space and…
Support for Institutional Projects
Element 3 supports Participating States in advancing national Positioning, Navigation and Timing initiatives across the full value chain. It provides ad-hoc assistance per country or domain to develop and promote GNSS and broader PNT-based products, applications, and services.
Next to funding, ESA may offer technical support in programme management, infrastructure development, and testing…
129 - Identification of Growth Opportunities in PNT Consumer Market
The global GNSS market is predicted to grow considerably in the next decade, with revenues coming from the sale of devices and even more services, and the wider PNT domain revenues are even bigger. Europe share in this market is around 23%, mostly in the professional markets, and it is not expected to increase. Except for few manufacturers located in Europe (e.g. uBlox and STM), the consumer…
128 - Resilient PNT Critical National Infrastructure case study
The rationale and context for this study are similar to as “EL1-120: Resilient PNT Critical National Infrastructure validation test bench”.
One of the considerations that can be derived by the analysis of the context is that the extent of the exposure of CNIs operators and suppliers to the risks posed by intentional and unintentional, natural and man-made RF interference threats is not very…
127 - Cross-Domain Nonlinear State Estimation for Autonomous Systems Using Unscented Kalman Filtering
Autonomous systems, whether operating on land, in the air, at sea, or in structured indoor environments, require robust, real-time state estimation to navigate complex, dynamic, and GNSS-challenged conditions. Traditional estimation techniques such as the Extended Kalman Filter (EKF) often rely on local linearization of the system dynamics and measurement models, which can result in degraded…
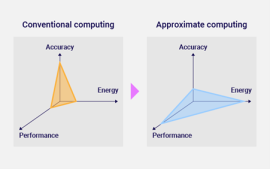
126 - Approximate Computing for Low-Power GNSS Signal Processing
Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) play a crucial role in providing accurate positioning, navigation, and timing information for a wide range of applications, ranging from daily mobile phone use to infrastructure and military activities. Nevertheless, GNSS receivers often require considerable computational resources to process the received GNSS signals, especially during the correlation…
125 - Receiver Architectures and Beam Scheduling Strategies for Fused- PNT Concept
The current and future LEO satcom constellations operating in Ku and Ka bands are considering, along with the provision of the main communication services, also a native provision of positioning, navigation, and timing (PNT) services. Leveraging the existing satcom frequency bands and signals, the concept of such integration is referred to as Fused PNT, promising increased resilience and…
124 - Optimisation of PVT engines for LEO measurement diversity
LEO-PNT stands out among the very promising evolutions of spaceborne PNT systems towards Multi-Layer Satellite Systems (MLSS), leveraging differentiators such as:
Whitening of measurements, in particular multipath;
More diverse opportunities to exploit doppler measurements in addition to ranging;
Faster transition between LOS and NLOS status, beneficial to the awareness of the…
123 - Quantum Magnetometer and algorithms for integrated Map Matching and Map Building
Magnetic crustal anomaly navigation is an alternative PNT technique which leverages the fact that the Earth’s crustal magnetic field exhibits spatial variations that can serve as a unique “fingerprint” for positioning. With sufficient sensitivity, these anomalies can be measured and matched to reference maps, enabling navigation in environments where other signals are unavailable or…
122 - Acoustic arrays for Drones localization and identification
Drones, or Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs), have evolved from defence applications into versatile platforms used across industries. They can fly autonomously or via remote control and are equipped with sensors and payloads for tasks such as crop monitoring, infrastructure inspection, environmental surveillance, logistics, and emergency response. As drone technology advances, features like AI,…